

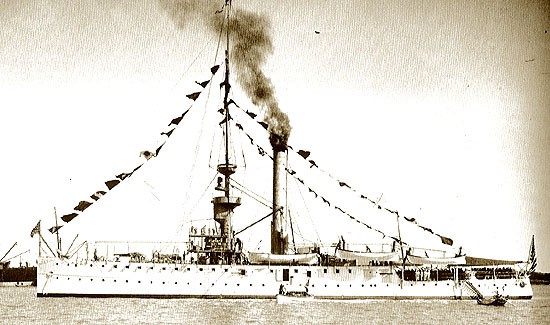
After initially serving in the North Atlantic, the approah of the Spanish American War found HELENA in Lisbon, Portugal. She was ordered to Key West, and then to Cuba to take part in the naval blockade. The gunboat escorted the Army's Fifth Corps transports from Florida to Cuba, and bombarded Siboney (Ensenada de los Altares) as a feint while troops were being landed at Daiquiri. HELENA also took part in the shelling of Spanish blockhouses and fortifications near Tunas on July 2 and 3, 1898, where she also towed the grounded transport FLORIDA to safety. On July 18, she took part in the assault on Manzanillo, Cuba, aiding in the destruction of eight small Spanish vessels. On July 24, HELENA was ordered to intercept the steamer CATALINA, but instead found the MIGUEL JOVER, bound for Bareclona with a load of cotton and staves. The vessel was captured as a prize.
After the armistice was agreed to between the U.S. and Spain, the need for vessels at Cuba lessened, however, there was a concern about the situation in the Philippines. HELENA was transferred to the Pacific, where she would serve the remainder of her career. She departed from Boston, Massachusetts on November 3, 1898 and proceeded to Manila via the Suez Canal. She arrived on February 10, 1899, six days after the Philippine American War began. She took an active part in the conflict, being present at the evacuation of Jolo and the landing of American forces, taking part in actions in Cavite Province, and in the bombardment of San Fabian in Lingayen Gulf. Her landing parties also aided in the capturing of Filipino defensive lines along the Zapote River.
Between October, 1900 and April 19, 1905, HELENA served variously between China and the Philippines, being placed out of commission on the latter date at Cavite. The following year, HELENA was recommissioned. Beginning in June of 1907, she began service in China, serving variously in the Yangtze River Patrol, and on the South China patrol. She continue in this role through her reduced commissioning on June 29, 1929 to her final decommissioning on May 27, 1932.
HELENA was sold on July 7, 1934.

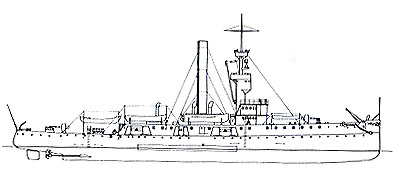
| Classification: | Gunboat | |
|---|---|---|
| Keel Laid: | October 11, 1894 | |
| Launched: | January 30, 1896 | |
| Commissioned: | July 8, 1897 | |
| Rig: | One military mast | |
| Armament: | Eight 4 inch rapid fire guns | |
| Four 6 pounder rapid fire guns | ||
| Four one-pounder rapid fire guns | ||
| Two Colt revolving cannons | ||
| One 3 inch field gun | ||
| Contractor: | Newport News Shipbuilding and Dry Dock Co., Newport News, Virginia | |
| Length: | 250 feet, 9 inches | |
| Beam: | 40 feet, 11 inches | |
| Mean draft: | 9 feet | |
| Displacement: | 1,397 tons | |
| Complement: | 10 officers and 165 enlisted men, under the command of Commander W. T. Swinburne. | |
| Engine type: | Twin vertoical triple expansion engines powering twin screws, and capable of generating 1,988 horsepower | |
| Boiler type: | six single-ended cylindrical boilers | |
| Coal Bunker Capacity | 274 tons | |
| Normal Coal Supply | 100 tons | |
| Speed: | 15,50 knots | |
| Endurance at 10 knots | 2,200 nautical miles | |
| Armor: | Watertight deck was had 3/8" armor on the slopes | |
| and 5/16" armor on the flat portion. | ||
| Cost | $280,.000 |
Alden, Cmdr. John D., USN (Ret.), American Steel Navy, (Annapolis: United States Naval Institute Press, 1972) 163, 166, 378.
Clerk of Joint Committee on Printing, The Abridgement of Message from the President of the United States to the Two Houses of Congress. (Washington: Government Printing Office, 1899) Vol II, 1100, 1190, 1191, 1250, 1251
Dictionary of American Naval Fighting Ships. Vol. III (Washington: Navy Department, 1977) 287.
McSherry, Jack, USN, Retired, Things We Remember. (Printed privately in 1966).
Spears, John R., Our Navy in the Spanish American War. (New York: Charles Scribner's Sons, 1898) 131-132, 280.